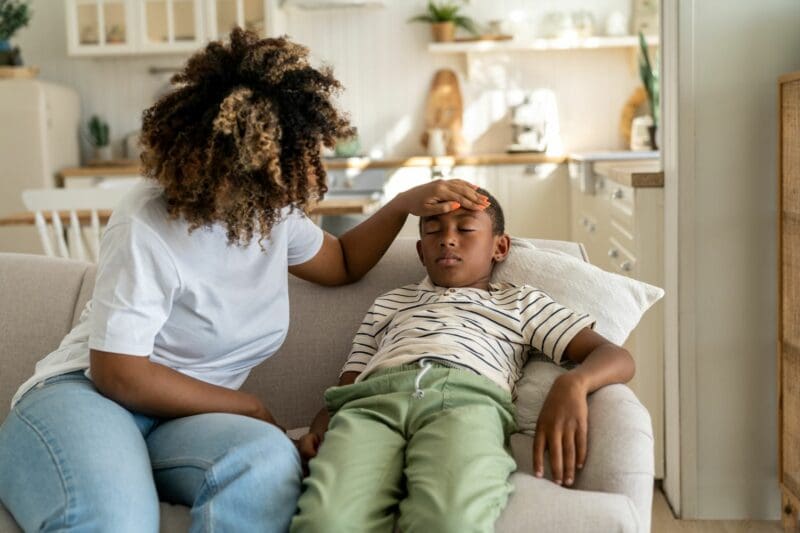

Common Childhood Illnesses
This article talks about the different illnesses that are prevalent in childhood.
Parents and caregivers of babies and toddlers are welcomed to read this.
Respiratory Infection
Respiratory infections like the common cold are among the most frequent illnesses in children, causing runny noses, coughs, and congestion. Young children typically experience 6-8 colds per year as their immune systems develop.
What to Do:
• Keep him hydrated with lots of fluids like water and low-sugar juices
• Keep him away from crowded places, sick individuals and other children
• Teach your child to use a tissue to blow his nose, or to cover his mouth when sneezing
• Bring your child to the doctor if he does not get better after a few days, or if he is also running a high fever
Ear Infection(Otitis Media)
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. This occurs when fluid builds up behind the eardrum, often following a cold. They’re particularly common in toddlers and can cause significant pain and temporary hearing difficulties.
What to Do:
- Give your child antibiotics or painkillers as prescribed by the doctor, Let the doctor know if the pain gets worse
Gastroenteritis
This is a very common condition that causes diarrhea and vomiting. It’s usually caused by a bacterial or viral tummy bug. It involves inflammation of the stomach and intestines, usually caused by viruses or bacteria. Children experience vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach cramps, with dehydration being the primary concern.
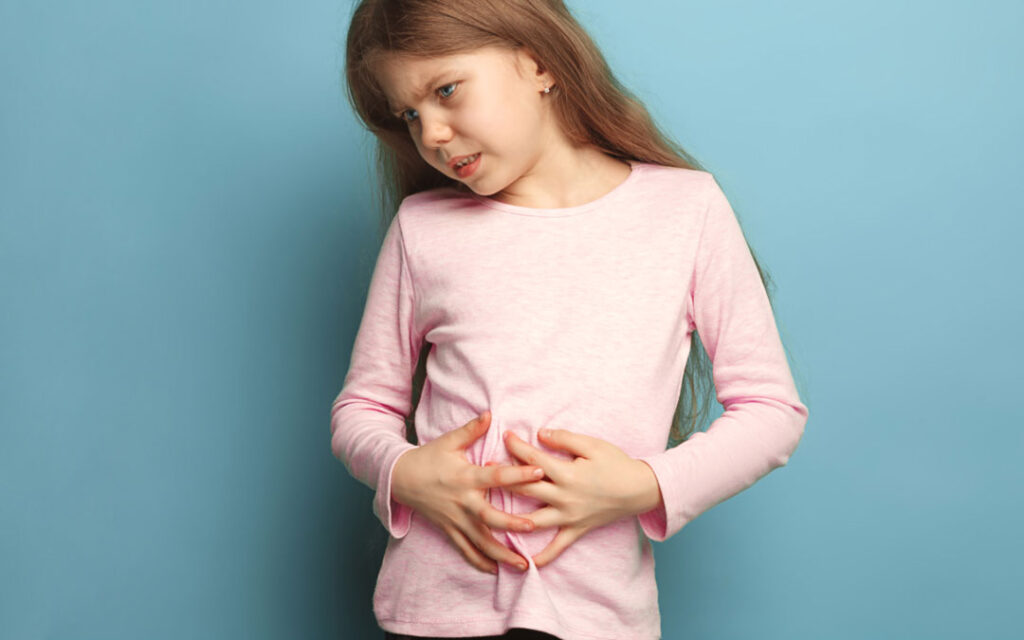

What to Do:
To replace lost water and salts, keep your child hydrated with fluids like water or juices that do not contain milk. Encourage your child to take frequent, small sips of fluids
• Avoid other people — stomach flu is contagious
• Bring your child to a doctor when symptoms persist or worsen
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease
This is a viral infection that creates painful blisters in the mouth and on the hands and feet. It spreads easily in daycare settings and typically resolves within a week.
What to Do:
• Inform your child’s school, infant or child care centre if he has HFMD. Keep your child home so that the infection won’t spread to other children
• Keep your child hydrated. Give him plenty of water and fluids
• Switch to a soft diet (e.g. porridge) as mouth ulcers can be very painful
• Help your child get plenty of bed rest
Chicken Pox( Varicella)
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella zoster virus, a member of the herpesvirus family. It causes an itchy rash of fluid-filled blisters across the body, along with fever and fatigue. While less common now due to vaccination, it remains highly contagious when it occurs.
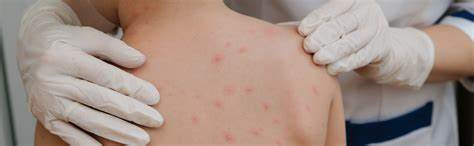
What to Do:
• Inform your child’s school or childcare centre if he has chickenpox and keep him home to prevent the illness from spreading to other children
• To avoid scratching, trim your child’s fingernails and consider letting him wear gloves at night
• Give your child cool baths to help relieve itching
• Bring your child to the doctor immediately if the rash spreads to the eye, or gets very red or tender. Also have your child see the doctor if he is dizzy, disoriented, vomiting, experiencing rapid heartbeat, short of breath, or if he is having tremors, loss of muscle coordination, a stiff neck or a high fever
Strep Throat
Strep Throat is a bacterial infection causing severe sore throat, fever, and swollen lymph nodes in children. Unlike viral sore throats, strep requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications.
What to Do:
• Avoid common triggers, such as exposure to cold, dust, pollen, animal fur, tobacco smoke and stress
• Bring your child to the doctor immediately if the symptoms are not relieved or have worsened.
Bronchiolitis
Bronchiolitis is caused by a viral infection, usually affecting children younger than two years of age.
It affects the small airways in the lungs, primarily in infants and toddlers. It causes wheezing, coughing, and difficulty breathing, often requiring careful monitoring of oxygen levels.
What to Do:
Keep your child hydrated with fluids like water and juices high in vitamin C
• Avoid smoky places. Tobacco smoke can make your child’s condition worse
• Bring your child to a doctor if he is wheezing for the first time or if his breathing is labored, and if he is lethargic, lacks energy or refuses to eat
Conjunctivitis(Pink Eye)
Conjunctivitis is the inflammation of the eye’s outer membrane, causing redness, discharge, and irritation. It can be viral, bacterial, or allergic, with bacterial forms requiring antibiotic treatment.
What to Do:
- Wash your hands regularly with warm soapy water
- Wash your pillow cases and face cloths in hot water and detergent
- Cover your mouth and nose when sneezing and put used tissues in the bin
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects a part of the urinary tract. It occurs when bacteria enter the urinary system, causing pain during urination, frequent urination, and sometimes fever. They’re more common in girls and require prompt antibiotic treatment.
What to Do:
- Go to the toilet as soon as you need to pee
- Always empty your bladder fully
- Stay well hydrated
- Wipe your bottom from front to back when you go to the toilet
Impetigo
This is a superficial bacterial skin infection that creates honey-crusted sores, typically around the mouth and nose. It spreads easily through direct contact and responds well to antibiotic treatment.
These conditions vary in severity and treatment requirements, so consulting with a pediatrician is important for proper diagnosis and care.
What to Do:
• Keep your child’s skin moisturized and use a topical steroid cream if prescribed by the doctor
• Avoid common triggers, such as sudden changes in temperature, dust, animal fur, tobacco smoke and stress
• Use mild soaps and dress your child in light cotton clothing
• Bring your child to the doctor if it interferes with his daily activity or sleep.

